A saas operations engineer is a specialized IT professional responsible for managing, monitoring, and optimizing Software-as-a-Service applications throughout their lifecycle. Here’s what defines this critical role:
Key Responsibilities:
- Monitor production SaaS environments for performance and reliability
- Manage user provisioning, access control, and security policies
- Handle incident response and troubleshooting for SaaS platforms
- Optimize costs and eliminate redundant software licenses
- Ensure compliance with data protection and industry regulations
- Automate deployment, configuration, and maintenance processes
Essential Skills:
- Cloud platform expertise (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Scripting and automation (Python, PowerShell, Bash)
- Database management (SQL, NoSQL)
- Containerization and microservices knowledge
- Strong problem-solving and communication abilities
The SaaS industry has exploded, growing by about 500% in recent years. Behind every reliable cloud service is a team of dedicated professionals: the unsung heroes of modern software delivery.
When your favorite app loads instantly and your business tools never go down, that’s the work of SaaS operations engineers. They keep the digital world spinning, preventing problems behind the scenes.
“Converting new customers is more expensive than retaining them for SaaS companies,” which makes the operational excellence these engineers provide critical for business success. With over 10,000+ SaaS operations engineer jobs available in the United States alone, the demand for this expertise has never been higher.
I’m Aleksandr Volodarsky. I’ve spent years scaling tech companies, including growing lemon.io from $2.7M to $10M. I’ve seen how crucial these roles are for building reliable platforms. Let me walk you through what makes these professionals so valuable.
Decoding SaaS Operations: The Engine Room of Modern Software
What keeps your favorite online tools running smoothly? That’s SaaS operations, or SaaSOps. Think of it as the engine room of a SaaS business, ensuring every system runs perfectly.
SaaSOps involves managing, monitoring, and optimizing the entire lifecycle of SaaS applications. As we rely more on digital tools like SaaS, proactive management is essential. SaaSOps integrates system monitoring, data security, and customer support into the service, ensuring tools are reliable, adaptable, and scalable by leveraging Cloud Computing.
What is a SaaS Operations Engineer?
The SaaS operations engineer tends to this digital engine room. It’s a hybrid role blending skills from software development, IT operations, and cloud infrastructure. Their core mission is to ensure SaaS applications run flawlessly, reliably, and efficiently.
As guardians of uptime and performance, they bridge the gap between development code and the infrastructure it runs on, ensuring a smooth customer experience. The demand for these roles is high, with over 10,000+ SaaS Ops Engineer jobs available in the US alone. They are vital in today’s tech world.
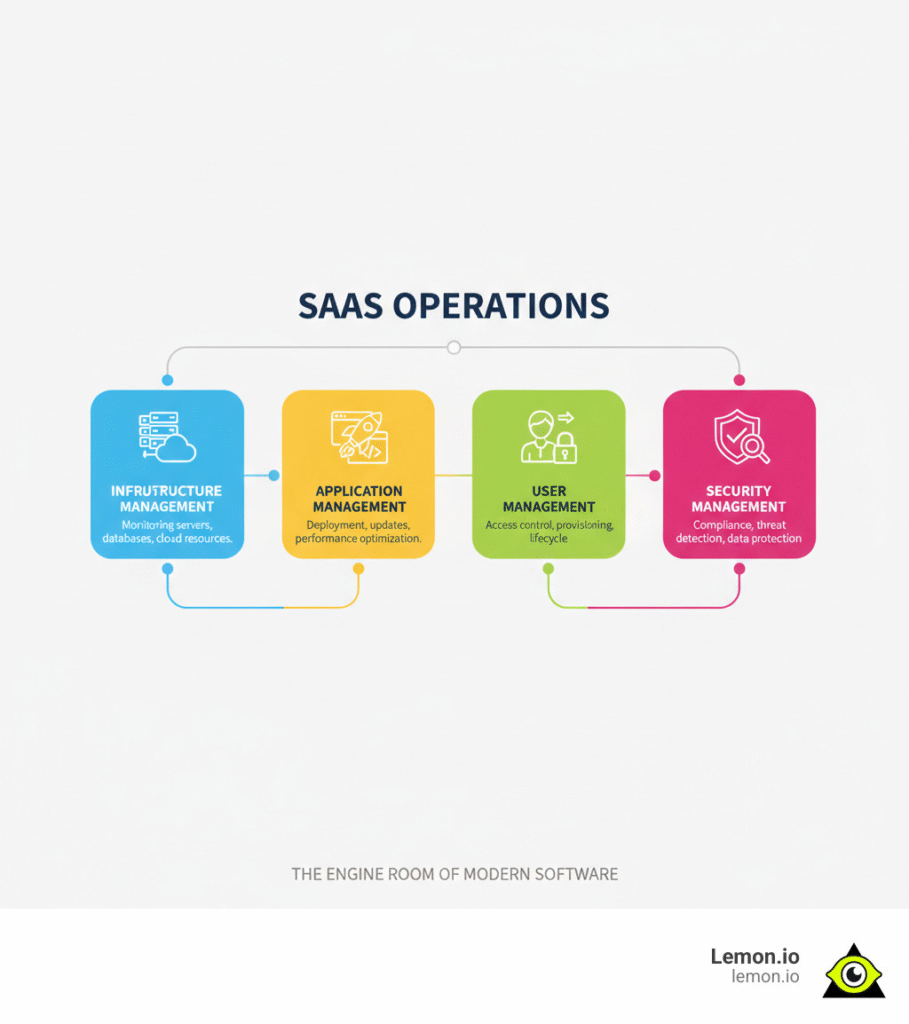
The Core Components of SaaSOps
SaaSOps has several core components that define a SaaS operations engineer‘s responsibilities:
Infrastructure Management involves overseeing the cloud foundation—servers, networks, and storage. It ensures that SaaS Deployment is set up and integrated correctly for a secure, high-performing environment.
Application Management focuses on the applications themselves. It covers integrations with other tools, regular tune-ups, fixing glitches, and rolling out new features without disruption.
User Management is about how users access applications. It includes managing accounts, setting permissions via role-based access control, tracking usage, and simplifying onboarding and offboarding.
Security and Governance is paramount for protecting data and adhering to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. This involves implementing security policies, monitoring for threats, and conducting regular audits.
Cost Optimization is about getting the best value from SaaS tools. This includes managing subscriptions and identifying unused licenses to ensure every investment is working for the business.
A Day in the Life: Key Responsibilities of a SaaS Operations Engineer
A saas operations engineer‘s day is a dynamic blend of firefighting, detective work, and strategic planning. They might start by checking overnight alerts and performance dashboards.

No two days are alike. One moment they’re optimizing database queries, the next they’re troubleshooting a critical production issue. This variety makes the role both challenging and rewarding.
Their work touches the entire SaaS ecosystem, from infrastructure to automation. As guardians of uptime and performance, they often prevent problems before users are even aware of them.
Infrastructure and Platform Management
Solid infrastructure management is the foundation of a saas operations engineer‘s work.
System monitoring is a daily routine. They use comprehensive monitoring solutions to track server health and application response times, acting as an early warning system to prevent customer impact.
Performance optimization involves hunting down bottlenecks when an application is sluggish. This could mean fixing a slow database query or rebalancing cloud resources to handle traffic.
Cloud platform management means ensuring the infrastructure can adapt as the business grows. This includes configuring auto-scaling groups, managing load balancers, and optimizing storage.
Database management ensures data flows smoothly and securely, from fine-tuning SQL queries to managing NoSQL clusters and planning for disaster recovery.
Infrastructure as Code is key. Using IaC practices, they automate environment creation, ensuring consistency and reducing human error.
Application Deployment and User Support
With a solid infrastructure, the focus shifts to applications and users.
Application deployment is a carefully orchestrated process. New features and bug fixes must be deployed to production without disrupting the user experience, requiring careful planning and testing.
CI/CD pipeline maintenance enables rapid, reliable deployments. Engineers maintain the automated pathways for code to travel to production, and understanding how CI/CD works is crucial for development velocity and quality.
Troubleshooting and incident response is a critical, part of the job. As first responders to production issues, they use logs and metrics to diagnose and fix problems quickly.
L2 and L3 customer support involves handling complex technical issues that require deep system knowledge. These interactions provide valuable feedback for system improvements.
Runbook improvement and automation are ongoing missions. They constantly seek to automate manual processes and improve documentation to prevent future incidents and speed up response times.
Security, Compliance, and Cost Optimization
A saas operations engineer also focuses on security, compliance, and cost.
Data security involves implementing layered protection for sensitive information, including encryption, secure network configurations, and vigilance against threats.
Access management uses role-based access control to ensure users have appropriate access, balancing security with productivity.
Compliance audits are critical for meeting standards like SOC 2 or GDPR. Engineers ensure systems and processes are compliant and well-documented.
SaaS spend management combines technical and business skills. They track usage, identify unused licenses, and optimize contracts to save money.
Shadow IT mitigation involves finding secure, approved alternatives to unauthorized tools used by employees, balancing productivity with risk management.
The Modern Toolkit: Essential Skills for a SaaS Operations Engineer
A saas operations engineer needs a diverse skill set combining technical knowledge with strong problem-solving and communication abilities. It’s about using tools effectively to build resilient systems.
The best engineers are curious, flexible team players who constantly automate repetitive tasks. They are analytical problem-solvers who can also communicate complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
Foundational Technical Skills
These skills are the bedrock for a successful saas operations engineer.
Cloud platforms are the foundation. Expertise in designing, deploying, and managing applications on public, private, or hybrid clouds is essential, including knowledge of major providers and best practices.
Containerization revolutionizes deployment. Engineers use container technologies to package applications with all dependencies, ensuring consistency. Orchestration platforms then manage these containers at scale.
Scripting with languages like Python, Bash, and PowerShell enables automation. It allows engineers to manage configurations and build operational tools to handle tasks in seconds.
Database management skills for both SQL and NoSQL databases are crucial. This covers administration, optimization, backup strategies, and troubleshooting.
Networking knowledge of concepts like VPCs, subnets, and load balancers is fundamental to designing secure, performant cloud infrastructure.
Essential Tools of the Trade
The key to SaaSOps tools is not memorizing them all, but understanding the categories and how to adopt new solutions.
Configuration management tools ensure consistency across environments. They automate application deployment and server configuration in a repeatable way.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools allow engineers to define infrastructure as code, making it versionable, reviewable, and repeatable.
Monitoring tools are the eyes and ears of SaaS operations. Metrics dashboards provide real-time visibility, while log aggregators help with troubleshooting.
CI/CD tools power our automation pipelines to streamline building, testing, and deploying software, enabling rapid release cycles.
SaaS Management Platforms (SMPs) provide centralized visibility and control over a company’s many SaaS applications, helping manage SaaS sprawl, security, and costs.
Successful engineers combine these tools into cohesive workflows to improve productivity and reliability.
The Business Impact: Why SaaS Operations Are Crucial for Success
A great SaaS product isn’t enough. The real magic is in the operations, where saas operations engineers ensure everything runs smoothly.
Poor operations lead to crashes and security breaches. Excellent operations mean systems that scale effortlessly, update seamlessly, and stop threats proactively. This is the invisible hand of a great SaaSOps team.
The difference between proactive and reactive approaches can make or break a SaaS business. A proactive approach anticipates problems, while a reactive one only fixes issues after customers are frustrated. This proactive mindset builds customer trust, ensures business continuity, and creates a competitive advantage.
Driving Growth, Scalability, and Customer Retention
Solid SaaS operations directly impact the bottom line. Smooth operations lead to significant cost savings from streamlined processes. Since retaining customers is cheaper than acquiring them, reducing churn is a major financial win.
Improved flexibility and speed allow businesses to roll out features faster and respond to market changes with agility. This responsiveness provides a competitive edge.
Security improvements from proactive monitoring and updates protect data and build customer confidence, which is a key selling point in an era of frequent data breaches.
Scalability is where SaaSOps shines. A saas operations engineer ensures the infrastructure can handle growth seamlessly, providing a consistent experience for 100 users or 100,000.
These improvements lead to reduced customer churn. A reliable, performant, and secure service gives customers fewer reasons to leave, turning them into loyal advocates.
Tackling Common SaaSOps Challenges
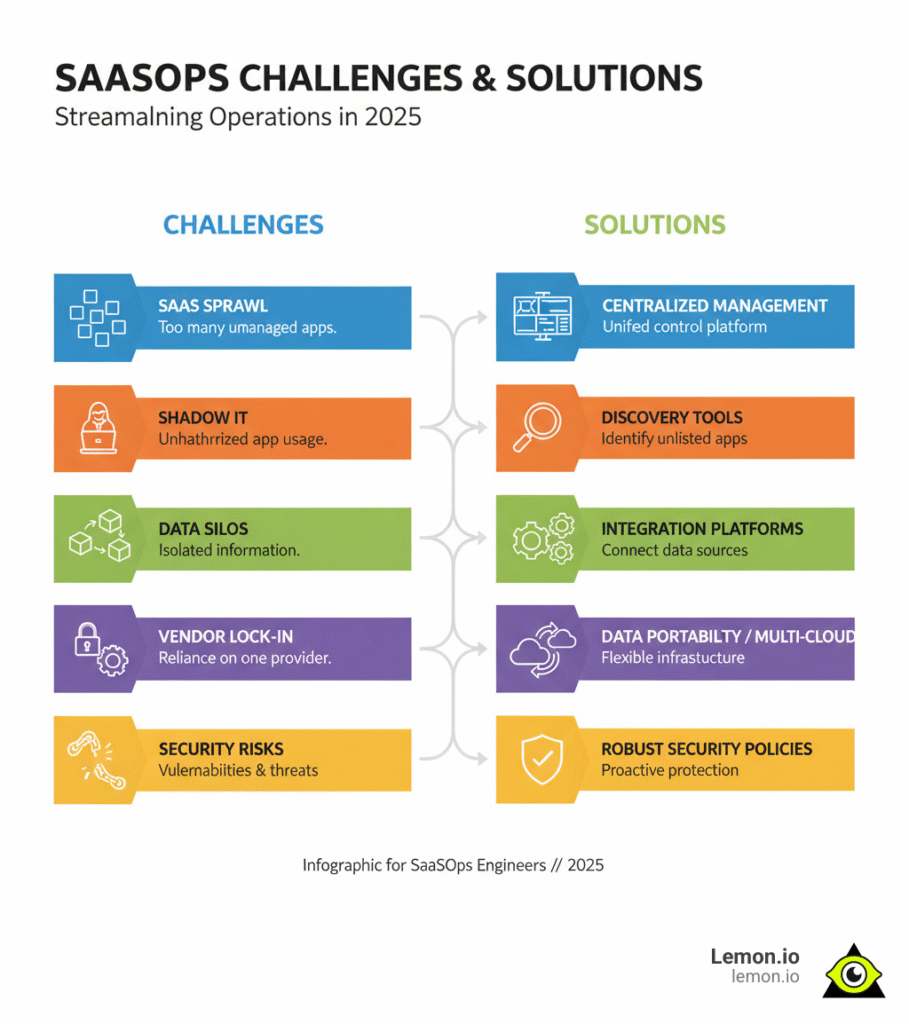
Growing companies face common operational challenges that can spiral without dedicated expertise. SaaS sprawl, the chaotic management of too many apps, is a primary issue that operations engineers solve with centralized oversight.
Shadow IT, where employees use unsanctioned tools, creates security risks and budget drain. A skilled saas operations engineer identifies these apps and provides secure alternatives. They also tackle data silos—isolated information pockets—through strategic integrations to create a unified business view.
To avoid vendor lock-in, they employ strategies like multi-cloud approaches. Finally, they mitigate the security risks that multiply with each new app by implementing comprehensive security policies and continuous monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions about the SaaS Operations Role
We love sharing insights into the incredible world of SaaS operations! Here are some of the most common questions we encounter.
What’s the difference between a SaaS Operations Engineer and a DevOps Engineer?
While these roles share skills, their focus differs. A saas operations engineer has a panoramic view, while a DevOps engineer has a focused lens.
A saas operations engineer manages the entire portfolio of an organization’s SaaS applications, including third-party solutions. Their mission is to ensure the reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness of all these tools for all end-users, covering user management, vendor relations, and compliance.
In contrast, a DevOps Engineer typically optimizes the development and deployment pipeline for a specific, in-house application. Their goal is to accelerate software delivery and automate infrastructure for that product.
In short, a DevOps engineer builds the road for one product, while a saas operations engineer manages the entire traffic system for all software. Both are vital but have different scopes.
What is the career path for a SaaS Operations Engineer?
The career path for a saas operations engineer is rich with opportunities for growth.
Professionals often start at a junior or mid-level, gaining experience in monitoring, troubleshooting, and automation. They can then progress to a Senior SaaS Operations Engineer role, leading complex projects and mentoring others.
For those who enjoy system design, the path can lead to SaaSOps Architect, responsible for large-scale strategies. Leadership-focused individuals can become a SaaSOps Manager or Director, overseeing teams and budgets, a role that blends technical and strategic skills like a Tech Lead but with a broader operational focus.
Specializations are also possible in security, cost management, or automation. The skills are highly transferable, offering great career flexibility. Understanding How to Hire a Software Developer can provide insight into what employers value.
What is the average salary for a SaaS Operations Engineer?
The saas operations engineer role is highly valued and commands competitive compensation, though the exact salary depends on several factors.
Key factors include experience level, with senior engineers earning more, and location, as major tech hubs offer higher salaries. Company size and type also play a role, with larger companies or well-funded startups often paying more. Finally, a specific skill set, such as expertise in niche technologies or advanced certifications, can increase earning potential.
While an exact average is hard to pinpoint, the role is recognized for its critical contribution. According to industry reports and surveys, compensation is attractive, especially at senior levels, making it a rewarding field both intellectually and financially!
Conclusion: Powering Your Product with Operations Expertise
The saas operations engineer is the quiet force behind every smooth digital experience. These unsung heroes keep the digital gears turning, ensuring robust infrastructure, seamless performance, and strong data security. Without them, the stability and growth of any SaaS company would be a far more challenging journey. They are the guardians of your customers’ happiness.
As the SaaS industry expands, the need for these specialists will grow. Future trends like AI for predictive insights and hyperautomation will make the role even more dynamic and vital.
For any business building reliable, scalable, and secure SaaS products, investing in top-tier saas operations engineer talent is essential. At Lemon.io, we understand this need. Our rigorous, 100% manual vetting process connects you with the top 1% of talent—experts ready to become the backbone of your SaaS operations.
Ready to find your own unsung hero? Hire vetted SaaS developers who can help your product not only survive but truly thrive in today’s competitive SaaS landscape.